Spinal Injection
Information for patients undergoing spinal injections
THE INFORMATION ON THIS PAGE IS AIMED to help answer some of the questions you may have about having a spinal injection. It explains the benefits, risks, and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
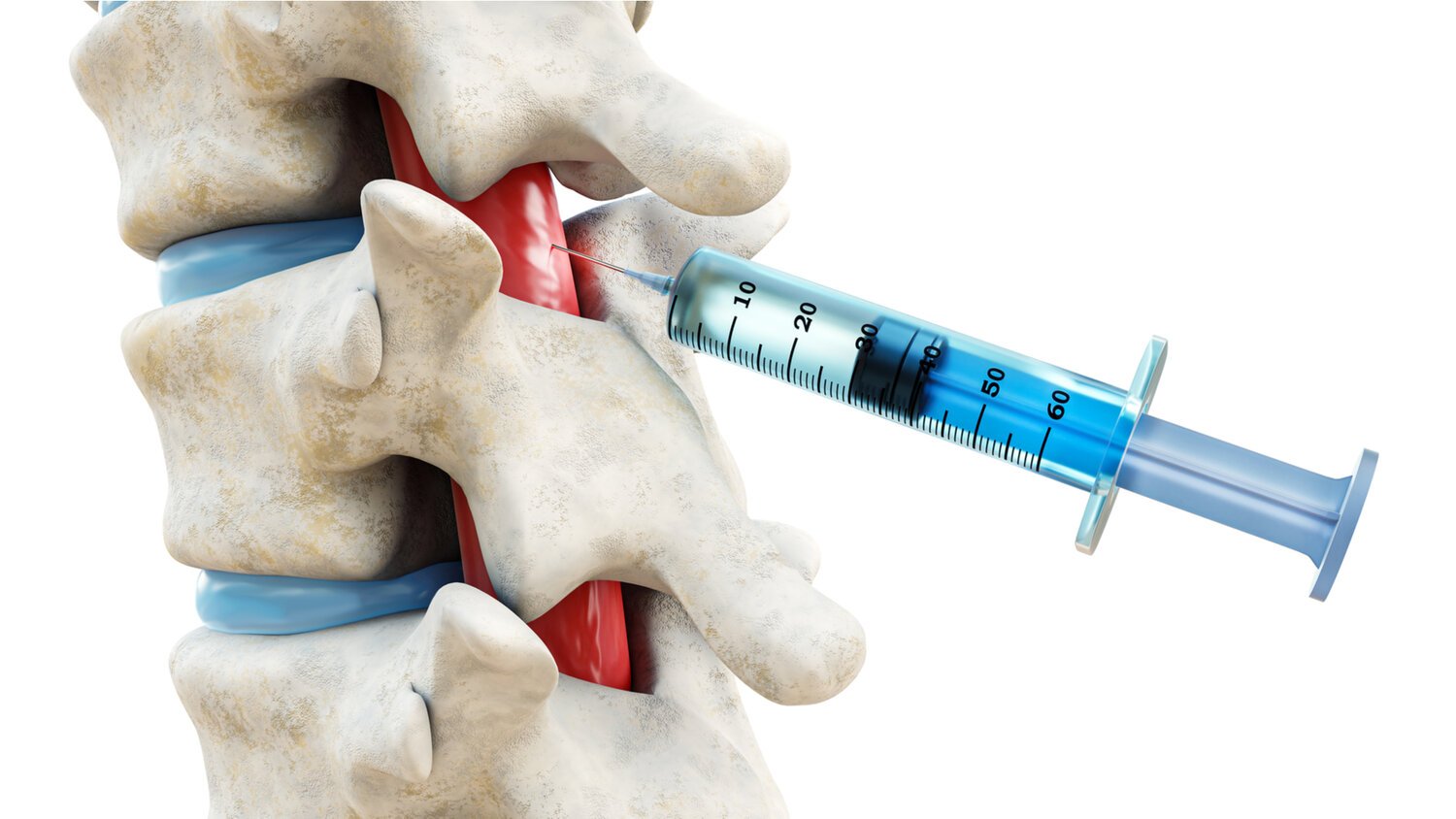
+ What is a spinal injection?
Your spine is made of a number of bones called vertebrae. They are connected to
one another allowing your spine to move and also protects the spinal
cord and nerves. These strong interconnections are made up of intervertebral
discs (which act as your spine’s shock absorbing system) and facet joints
(which connect the vertebrae to one another). These structures can wear down
and, with time, and cause pain.
There are two medicines used in spinal injections:
- Local anaesthetic : gives an immediate relief
- Steroid : Reduces inflammation in the injected area and can take 2 weeks to work fully.
A successful spinal injection can last up to three months.
Your spine is made of a number of bones called vertebrae. They are connected to one another allowing your spine to move and also protects the spinal cord and nerves. These strong interconnections are made up of intervertebral discs (which act as your spine’s shock absorbing system) and facet joints (which connect the vertebrae to one another). These structures can wear down and, with time, and cause pain.
There are two medicines used in spinal injections:
- Local anaesthetic : gives an immediate relief
- Steroid : Reduces inflammation in the injected area and can take 2 weeks to work fully.
A successful spinal injection can last up to three months.
+ Types of spinal injection (can be in the neck or back)
- Epidural injection targets the space that surrounds your spinal cord and disc.
- Facet or sacroiliac joint injection targets the joints that link the bones of your spine.
- Nerve root injection targets individual nerves in your spine.
- Electricity can also be used to prolong the pain relief. (Pulsed radiofrequency / Rhizotomy )
The type of spinal injection you have will be based on your specific symptoms.
- Epidural injection targets the space that surrounds your spinal cord and disc.
- Facet or sacroiliac joint injection targets the joints that link the bones of your spine.
- Nerve root injection targets individual nerves in your spine.
- Electricity can also be used to prolong the pain relief. (Pulsed radiofrequency / Rhizotomy )
The type of spinal injection you have will be based on your specific symptoms.
+ What are the benefits – why should I have a spinal injection?
Spinal injections are used to diagnose the cause of your pain and to
provide intermediate term pain relief. This can be repeated periodically to
allow you to progress with other treatments such as physiotherapy
Spinal injections are used to diagnose the cause of your pain and to provide intermediate term pain relief. This can be repeated periodically to allow you to progress with other treatments such as physiotherapy
+ What are the risks of a spinal injection?
In general, the risks relate to the anaesthetic and the spinal treatment
itself. Spinal injections are done with local anaesthetic and sedation
(to help you relax). Spinal injections are commonly performed and are
generally safe. If complications occur, they are usually mild and resolve
after about three weeks.
In general, the risks relate to the anaesthetic and the spinal treatment itself. Spinal injections are done with local anaesthetic and sedation (to help you relax). Spinal injections are commonly performed and are generally safe. If complications occur, they are usually mild and resolve after about three weeks.
+ Rare complications include:
Infection ( < 1 in 100) / Bleeding ( < 1 in 100 ) and or local
bruising / Headaches ( < 1 in 100)
Spinal nerve injury ( 1 in 100 ) This can lead to a temporary loss of
feeling or muscle weakness in the legs or bladder/bowel dysfunction.
Steroid side effects : hot flushes, mild abdominal pain, fluid retention,
a temporary rise in blood sugar, and menstrual irregularities (in women).
These should settle within a few days.
Infection ( < 1 in 100) / Bleeding ( < 1 in 100 ) and or local bruising / Headaches ( < 1 in 100)
Spinal nerve injury ( 1 in 100 ) This can lead to a temporary loss of feeling or muscle weakness in the legs or bladder/bowel dysfunction.
Steroid side effects : hot flushes, mild abdominal pain, fluid retention, a temporary rise in blood sugar, and menstrual irregularities (in women). These should settle within a few days.
+ Can everyone have spinal injections?
No, some people are not good candidates for spinal injections. This includes those with:
- Active infection (such as blood poisoning, chest or dental infection)
- Skin infection at the site of needle puncture
- Bleeding disorder or patients taking medicines to thin their blood (eg Warfarin/Plavix)
- Allergy to contrast, steroids or local anaesthetic.
- Poor medical health
No, some people are not good candidates for spinal injections. This includes those with:
- Active infection (such as blood poisoning, chest or dental infection)
- Skin infection at the site of needle puncture
- Bleeding disorder or patients taking medicines to thin their blood (eg Warfarin/Plavix)
- Allergy to contrast, steroids or local anaesthetic.
- Poor medical health
+ How can I prepare for a spinal injection?
Pls tell us if you have a bleeding disorder or take any of these blood
thinning medications such as (Warfarin/Plavix/Xarelto/Pradaxa/Eliquis/Lixiana).
Or if you are pregnant.
- Active infection (such as blood poisoning, chest or dental infection)
- Skin infection at the site of needle puncture
- Bleeding disorder or patients taking medicines to thin their blood (eg Warfarin/Plavix)
- Allergy to contrast, steroids or local anaesthetic.
- Poor medical health
Pls tell us if you have a bleeding disorder or take any of these blood thinning medications such as (Warfarin/Plavix/Xarelto/Pradaxa/Eliquis/Lixiana). Or if you are pregnant.
- Active infection (such as blood poisoning, chest or dental infection)
- Skin infection at the site of needle puncture
- Bleeding disorder or patients taking medicines to thin their blood (eg Warfarin/Plavix)
- Allergy to contrast, steroids or local anaesthetic.
- Poor medical health
+ What happens during the treatment?
You will be asked to sign a consent form. You will be taken to the
operating theatre. You will lie on your stomach or your back depending
on your injection site. A drip will be inserted for safety and for
sedation. You will be given sedation. After sterile cleaning of the
injection site, local anaesthetic is injected to make the area numb.
The injection needles are then carefully inserted into your spine using
an x-ray or ultrasound guidance. It is important that you do not move.
Local anaesthetic and steroids are then injected into your spine. If
using electricity, testing will be performed to ensure the correct
nerves/structures are targeted. The treatment takes around 10-20
minutes.
You may have some tenderness at the needle insertion site. This may
last a few hours. You can place an ice pack on the area to reduce the
discomfort, but for no longer than 20 minutes at a time. You should
never put ice directly on your skin as it can cause frostbite. It is
also common after this treatment to have an increase in pain for the
24 to 72 hours. You should not be alarmed by this. Your symptoms
should improve in the days following the spinal injection. The local
anaesthetic will keep you pain-free for a while, but it is best to
take things easy for the first 24 hours. After this, your back may
start to feel sore again because the steroids may take up to 2 weeks
to work. Patients after electricity treatment may have worse pain
for up to 2 weeks before gradual significant pain relief.
The spinal injection can work up to 3 months before you feel
some of symptoms recur.
You will be asked to sign a consent form. You will be taken to the operating theatre. You will lie on your stomach or your back depending on your injection site. A drip will be inserted for safety and for sedation. You will be given sedation. After sterile cleaning of the injection site, local anaesthetic is injected to make the area numb. The injection needles are then carefully inserted into your spine using an x-ray or ultrasound guidance. It is important that you do not move. Local anaesthetic and steroids are then injected into your spine. If using electricity, testing will be performed to ensure the correct nerves/structures are targeted. The treatment takes around 10-20 minutes.
You may have some tenderness at the needle insertion site. This may last a few hours. You can place an ice pack on the area to reduce the discomfort, but for no longer than 20 minutes at a time. You should never put ice directly on your skin as it can cause frostbite. It is also common after this treatment to have an increase in pain for the 24 to 72 hours. You should not be alarmed by this. Your symptoms should improve in the days following the spinal injection. The local anaesthetic will keep you pain-free for a while, but it is best to take things easy for the first 24 hours. After this, your back may start to feel sore again because the steroids may take up to 2 weeks to work. Patients after electricity treatment may have worse pain for up to 2 weeks before gradual significant pain relief.
The spinal injection can work up to 3 months before you feel some of symptoms recur.
+ What happens after the procedure?
Following the treatment you will be taken to the recovery department.
This is where you are monitored for the initial post-operative period.
You will then be transferred to the Dayward.
Your leg/arm may be heavy after the injection. You must not walk
unsupervised if that is the case. If you have any concerns about your
walking or controlling your bladder/bowel, you must tell a member of
staff. You will need to arrange for a responsible adult to accompany
you home.
Following the treatment you will be taken to the recovery department. This is where you are monitored for the initial post-operative period. You will then be transferred to the Dayward.
Your leg/arm may be heavy after the injection. You must not walk unsupervised if that is the case. If you have any concerns about your walking or controlling your bladder/bowel, you must tell a member of staff. You will need to arrange for a responsible adult to accompany you home.
+ What do I need to do after I go home?
It is essential that you continue to take painkillers as advised after
your treatment.
The plaster can be removed after 24 hours and you can then have a bath
or shower as normal. Before the plaster is removed, avoid getting the injection site wet.
Generally, there are no restrictions after your spinal injections once
the post-treatment pain has settled down. You should be able to return
to physiotherapy or other spinal exercises within a week of your injection.
Depending on the nature of your employment, you may wish to return to
work after 72 hours.
If your pain does not settle within four weeks, you can either be
reviewed in your scheduled outpatient appointment or you can contact
your GP for advice and pain management.
It is essential that you continue to take painkillers as advised after your treatment.
The plaster can be removed after 24 hours and you can then have a bath or shower as normal. Before the plaster is removed, avoid getting the injection site wet.
Generally, there are no restrictions after your spinal injections once the post-treatment pain has settled down. You should be able to return to physiotherapy or other spinal exercises within a week of your injection.
Depending on the nature of your employment, you may wish to return to work after 72 hours.
If your pain does not settle within four weeks, you can either be reviewed in your scheduled outpatient appointment or you can contact your GP for advice and pain management.
+ Will I have a follow-up appointment?
Yes, four weeks after your surgery. We will send you an appointment letter for review in Tallaght/Santry/ Vista in Naas.
Yes, four weeks after your surgery. We will send you an appointment letter for review in Tallaght/Santry/ Vista in Naas.
Contact details
Please contact your GP or attend your local A&E department if you have any urgent medical concerns outside office hours.
Please also have your insurance details available if you wish to use your health insurance.
The codes for injections are 5611 / 5612 / 5616. You can check with your insurer if you are covered in upmc Sports Surgery clinic, Tallaght University Hospital, bEACON HOSPITAL oR UPMC hospital, KILDARE.

